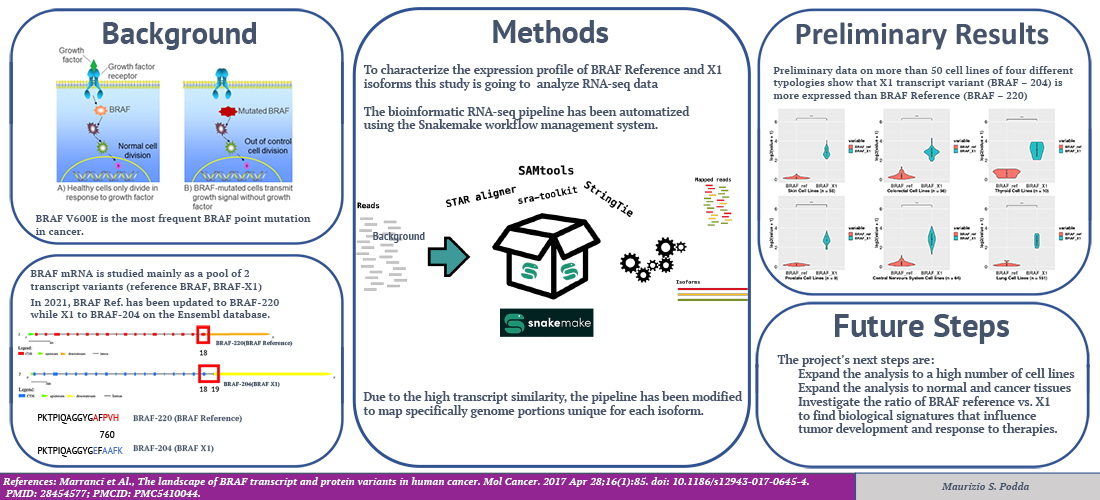
The BRAF protein kinase is widely studied as a cancer driver and therapeutic target. The BRAF V600E mutation is the most frequent BRAF point mutation. The 600 amino acid valine (V) is substituted by glutamic acid (E), which drives diagnoses such as melanoma, papillary thyroid carcinoma, colorectal cancer, and non-small-cell lung. This project aims at understanding whether differences in the ratio between two BRAF(V600E) transcript variants (called ref and X1, PMID: 28454577) are associated with differences in functional signatures, prognosis, and response to treatment. The project aims to refine a bioinformatic pipeline that allows quantifying the expression levels of BRAF-ref (BRAF-220) and BRAF-X1 (BRAF-204) mRNAs, starting from RNA-seq data. The bioinformatic RNA-seq pipeline is going to be automatized using the Snakemake workflow management system. Due to the high number of transcripts and the similarity between ref and X1, the RNA-seq analysis pipeline is going to be modified to map specific genome portions of the sequence, unique for each isoform, using customized GTF files. The project’s future steps are to expand the analysis to different cell lines, to normal and cancer tissues, and to investigate the ratio of BRAF reference and X1 to find biological signatures that influence tumor development and therapies.